Ad injection starts when users install an app or browser extension bundled with ad-injector software. Once the installation process is complete, the software will start injecting advertisements into the user’s browser.
Ad Insertion works by injecting unauthorized advertising into the user’s browsing experience. Malicious software does these things, such as adware or malware, installed on the user’s device. Installation of Adware through a variety of methods, such as downloading software from untrusted sources, clicking on malicious links, etc.
After the installation process of adware, it can introduce advertising into the user’s browsing experience in several ways. A standard method is to use a browser extension, which modifies a website’s HTML and CSS to display unauthorized ads. The adware can also intercept ad requests from the user’s browser and replace them with its own ads.
Insert ads targeted to specific websites or search queries, allowing scammers to show their ads to users interested in specific topics. In some cases, the adware may also track a user’s browsing behavior and use this information to deliver more targeted advertising.
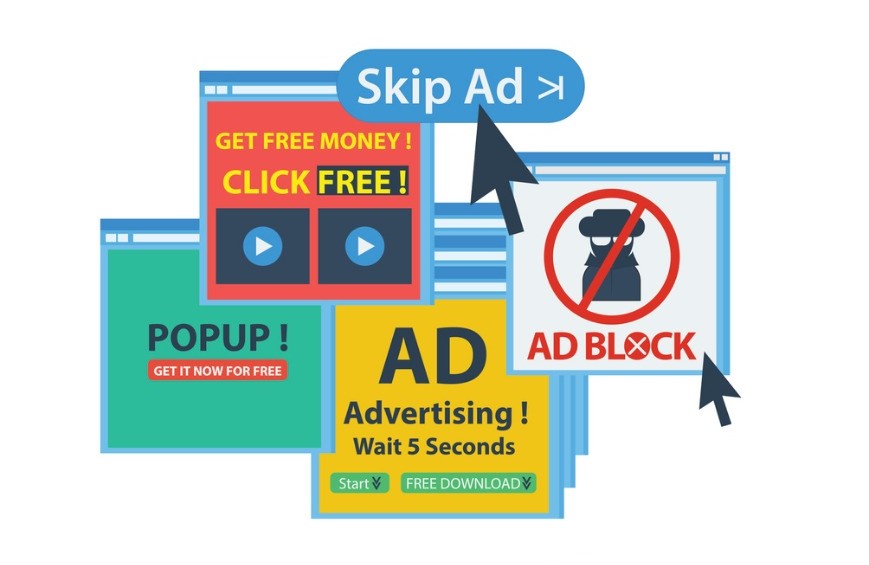
What is the purpose of ad insertion?
The purpose of ad insertion is to generate revenue for fraudsters using a display of their own ads. Rather than the legitimate ads that will display on the website. This can be harmful to both advertisers and publishers as it reduces the effectiveness of advertising campaigns and causes a loss of revenue for publishers.
Some of the most common examples of these extensions and software are PDF converters, browser screenshot extensions, ad blockers, etc.
Monetized through partnerships with third-party ad injectors pay affiliate fees every time at the install of the software.
Although ad insertion detection may be easy for some users. Many users cannot able to recognize the ads and are automatically redirected to ads on partner websites.